Leading sustainable transformation in healthcare: the case of Erasmus MC
Pioneering sustainable healthcare through the circular transformation of Intensive Care Units, enhancing both human and planetary health.
In collaboration with Erasmus Medical Center, Metabolic conducted a comprehensive study to transform the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) through a circular economy lens. Our joint efforts focus on reducing waste and emissions by redefining how medical products are used and disposed of in the ICU setting. This initiative aims to drastically reduce environmental impact while ensuring high-quality patient care, addressing both material and operational aspects of the ICU.
- Client: Erasmus Medical Center
- Date: 2022
Addressing sustainability in high-impact healthcare environments
Healthcare is an essential aspect of society that ensures the well-being of all individuals. However, it also significantly contributes to carbon emissions and other environmental impacts, notably through the lifecycle of medical products from production to disposal.
Leading sustainable transformation in the healthcare sector, Erasmus MC’s ICU committed to exploring reducing its environmental footprint while maintaining exceptional care standards, amid a global push towards sustainable healthcare practices – including the Dutch Green Deal for Sustainable Healthcare.
Implementing circular strategies to optimize ICU operations
The ICU at Erasmus MC faced dual challenges: managing the high consumption of single-use medical supplies and the need for a more sustainable operation model. We worked together aiming to implement a circular approach to reduce waste and environmental impact without compromising patient care quality.
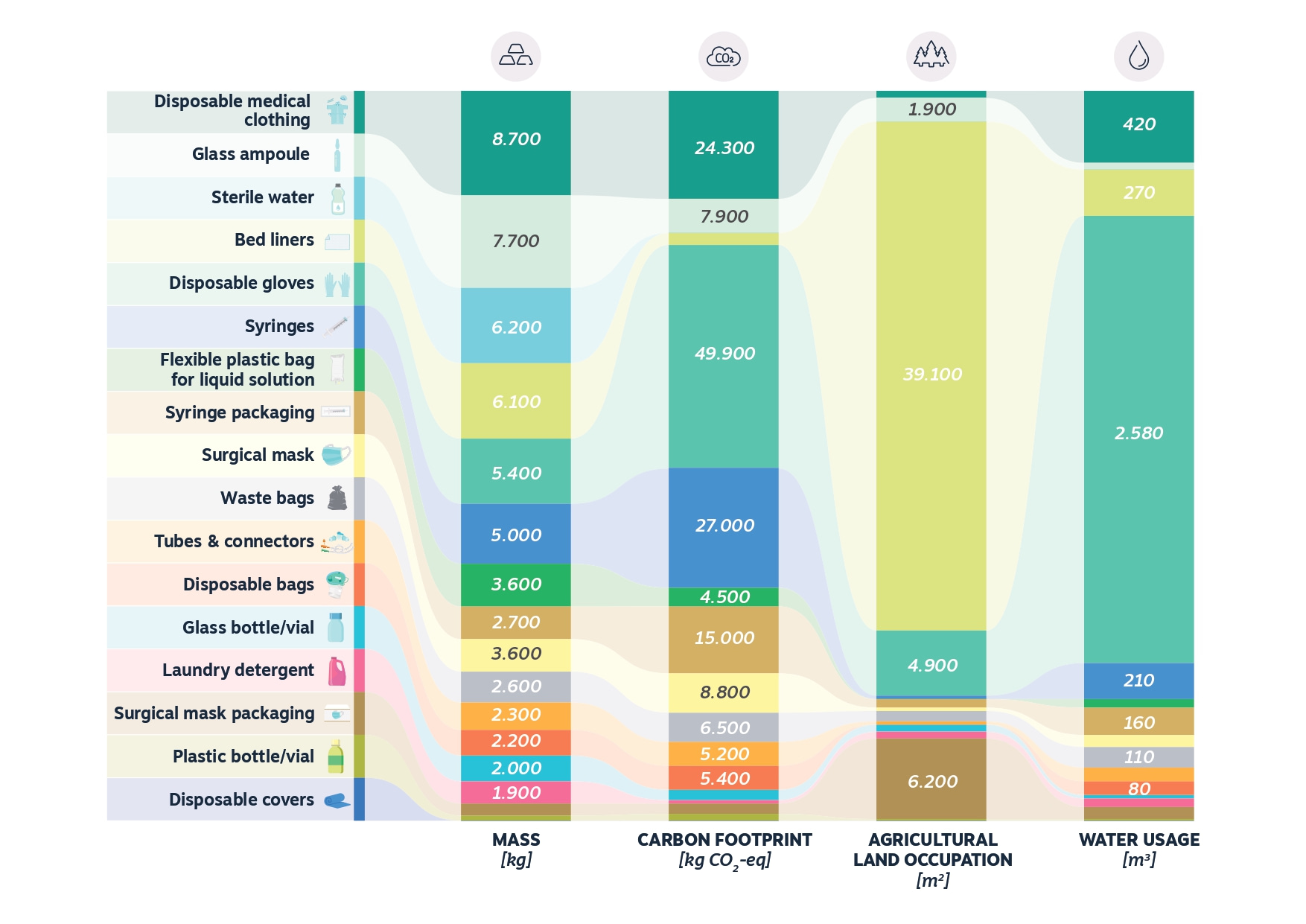
Metabolic conducted detailed material flow analyses and impact assessments to identify material and operational hotspots within the ICU. Relating them to the products used, we facilitated the development of targeted interventions.
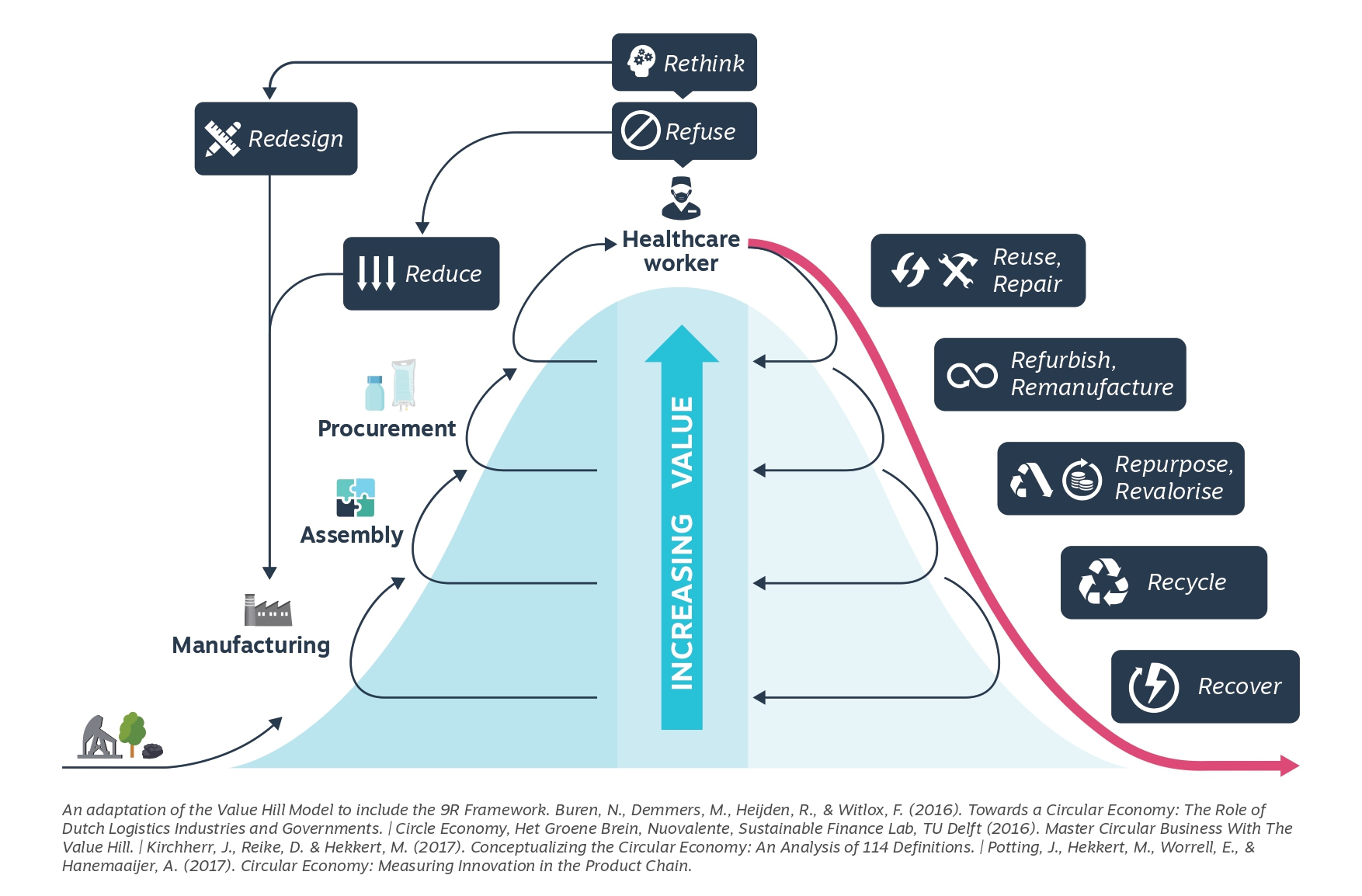
By applying the Value Hill model and 9R strategies—ranging from refuse and reduce to recycle and recover—we proposed systemic changes across the product lifecycle to enhance circularity in daily ICU operations. This analysis highlights challenges and opportunities for implementing circular strategies across the medical sector, aiming to retain the value of products and materials within the ICU, reduce environmental impacts, and ensure resilient operation.
A sustainable model for future healthcare
Our collaboration led to a strategic plan outlining immediate, medium-term, and long-term actions to integrate circular principles into the ICU. The project resulted in a set of actionable recommendations for Erasmus MC to transition towards a circular ICU model. These include optimizing resource use, extending the life cycle of medical equipment, and implementing sustainable procurement practices, setting a precedent for healthcare institutions worldwide.
This baseline assessment also led to follow-up research projects from students at TU Delft on priority products, including gloves and syringes.
- Check out the news on the Erasmus MC website
- Circular material flow in the intensive care unit—environmental effects and identification of hotspots
- Dutch Green Deal for Sustainable Healthcare
- Follow-up research from TU Delft students is collected here. More details:
- Curious to learn more about how circular strategies look in the value chain? Check this interactive page.